Digital Literacy: Driving Member Engagement Success

Most british and Canadian membership organisations now recognise that over sixty percent of executives view digital literacy as vital for future growth. Digital skills are no longer just a technical requirement but shape how nonprofits engage members and operate efficiently. With members expecting smarter digital interactions and staff needing to manage evolving technologies, understanding digital literacy unlocks practical strategies to drive stronger engagement, boost operational results, and support ongoing organisational success.
Table of Contents
- Defining Digital Literacy For Modern Organisations
- Core Digital Skills And Key Competencies
- Digital Literacy In Member-Centric Operations
- Risks Of Poor Digital Proficiency
- Building A Future-Ready Membership Organisation
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Importance of Digital Literacy | Digital literacy is essential for modern organisations, requiring continuous adaptation and critical thinking beyond basic technology skills. |
| Inclusivity in Skill Development | Strategies must address diverse workforce demographics to ensure equitable access to digital competency training. |
| Risks of Poor Proficiency | Inadequate digital skills can lead to reduced engagement, operational inefficiencies, and compliance failures, particularly impacting older workers and those with lower education levels. |
| Future-Ready Organisations | Embracing digital acceleration involves developing a culture of continuous learning and investing in member-focused technological innovations. |
Defining Digital Literacy for Modern Organisations
Modern organisations increasingly recognise digital literacy as a critical capability beyond basic technological competence. Digital competencies now represent comprehensive skills enabling professionals to navigate complex digital interactions, manage information effectively, and participate meaningfully in technology-enabled environments.
At its core, digital literacy encompasses multiple interconnected dimensions. These include technical proficiency, critical thinking about digital information, understanding privacy and security protocols, and the ability to communicate and collaborate using digital platforms. Unlike traditional digital skills, contemporary digital literacy demands adaptive learning – continuously updating one’s capabilities to match rapidly evolving technological landscapes.
UNESCO’s framework highlights that digital literacy must transcend age, professional background, and technological access. Organizations must develop inclusive strategies that support skill development across diverse workforce demographics. This means creating learning pathways that address individual differences while maintaining consistent standards of digital competence. Digital interactions require nuanced understanding of technological tools, information validation, and ethical digital engagement.
Pro tip: Conduct regular digital literacy assessments to identify skill gaps and design targeted training programmes that enhance your organisation’s technological adaptability.
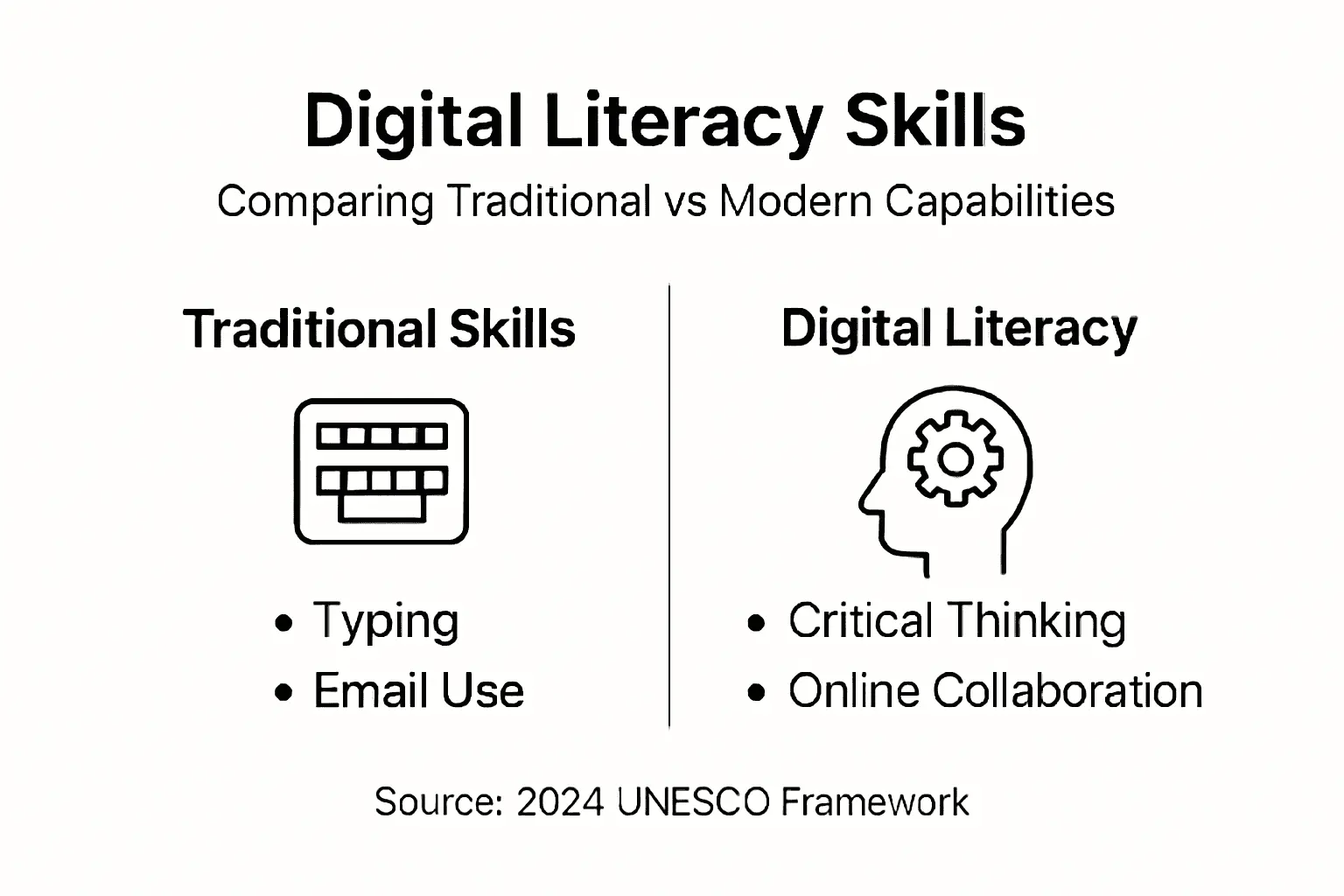
The following table contrasts traditional digital skills with modern digital literacy in organisational contexts:
| Aspect | Traditional Digital Skills | Modern Digital Literacy |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Basic technology usage | Adaptive, critical, continuous |
| Information Handling | Simple searches, emails | Validation, curation, synthesis |
| Security Awareness | Passwords, antivirus | Privacy protocols, risk assessment |
| Communication | Email, static content | Interactive, multi-platform |
| Learning Approach | One-off training | Lifelong, self-directed, inclusive |
Core Digital Skills and Key Competencies
Modern membership organisations require a robust framework of digital competencies that extend far beyond basic technological understanding. European digital skills recommendations emphasise five critical capability domains: information literacy, digital content creation, online safety, problem-solving, and effective communication.

These core digital skills are not static but dynamic capabilities that demand continuous adaptation. Professionals must develop sophisticated abilities such as critically evaluating online information, understanding privacy protocols, managing digital resources effectively, and collaborating through technology-enabled platforms. Digital competence frameworks now prioritise ethical technology usage, emphasising the importance of digital citizenship and responsible online interactions.
Successful digital skill development requires a holistic approach that integrates technical training with broader cognitive capabilities. Organizations must create learning pathways that support individual growth, address diverse technological skill levels, and foster an environment of continuous learning. This means designing inclusive programmes that help members develop not just technical proficiency, but also critical thinking, creativity, and adaptive technological understanding.
Pro tip: Implement a structured digital skills assessment programme that identifies individual competency gaps and provides personalised learning resources to enhance technological capabilities across your organisation.
Digital Literacy in Member-Centric Operations
Membership organisations are increasingly transforming their operational strategies through digital literacy, recognising its critical role in creating meaningful, personalised member experiences. Digital acceleration research highlights the profound impact of data-driven approaches in maintaining productive member relationships while balancing privacy and engagement expectations.
At the heart of member-centric digital operations lies the ability to leverage collaborative technologies effectively. Digital literacy enables organisations to develop sophisticated communication strategies that enhance social proximity, build trust, and create more responsive interaction models. Hybrid work environment studies demonstrate how advanced digital competencies support organisational cohesion, allowing members to feel connected and valued, even in increasingly dispersed and digital-first environments.
Successful implementation requires a strategic approach to digital literacy that goes beyond technical skills. Organizations must cultivate an ecosystem of continuous learning, where members and staff develop adaptive digital capabilities. This involves creating comprehensive training programmes, investing in user-friendly technologies, and developing policies that support ethical data usage and digital collaboration. The goal is to transform digital literacy from a technical requirement into a core organisational competency that drives engagement, innovation, and member satisfaction.
Pro tip: Develop a personalised digital literacy roadmap for each member segment, using adaptive learning technologies to address individual skill levels and professional development needs.
Risks of Poor Digital Proficiency
Poor digital literacy represents a significant threat to organizational effectiveness and individual professional development. Systematic research reveals that inadequate technological skills create profound barriers to participation in modern knowledge economies, undermining both institutional performance and personal employability.
The consequences of limited digital proficiency extend far beyond simple technological incompetence. Demographic digital skills analysis demonstrates that specific population segments – particularly older workers and individuals with lower formal education – face substantially increased risks of digital exclusion. These risks manifest through reduced access to critical services, diminished career opportunities, and increased social isolation, creating systemic challenges for organizations seeking to maintain competitive and inclusive environments.
Membership organizations must proactively address digital skill disparities by developing comprehensive upskilling strategies. This requires implementing targeted training programmes, creating supportive learning environments, and designing adaptive technological interventions that accommodate diverse skill levels. By recognising digital proficiency as a critical organizational capability, leaders can mitigate risks, enhance member engagement, and create pathways for continuous professional development that transcend traditional technological barriers.
Here is a summary of the risks organisations face due to inadequate digital proficiency:
| Risk Area | Organisational Impact | Affected Demographics |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Exclusion | Lower engagement, lost members | Older workers, less-educated |
| Productivity Loss | Operational inefficiency | Teams lacking up-to-date skills |
| Compliance Failure | Legal/regulatory breaches | Staff unaware of privacy rules |
| Reputation Damage | Trust erosion, negative public image | Members facing digital barriers |
Pro tip: Conduct regular digital skills audits to identify skill gaps and develop personalized learning pathways that address individual member technological competencies.
Building a Future-Ready Membership Organisation
Digital acceleration has become a critical imperative for membership organisations seeking sustainable growth and relevance. Future-ready strategies demand a comprehensive approach that integrates technological innovation, data-driven insights, and adaptive organizational capabilities.
Successful future-ready organisations must develop a holistic digital transformation strategy that transcends technological implementation. This involves creating a culture of continuous learning, where digital literacy becomes a fundamental organizational competency. Key focus areas include developing agile technological infrastructure, fostering data privacy and ethical use, and creating personalised member experiences that leverage advanced digital tools and artificial intelligence.
The transition requires a multifaceted approach that balances technological investment with human-centric design. Organizations must develop robust digital ecosystems that enable seamless communication, provide adaptive learning opportunities, and create value-driven engagement models. This means investing in digital skills training, implementing flexible technological platforms, and maintaining a strategic focus on member needs and emerging technological trends.
Pro tip: Create a dedicated digital transformation taskforce with representatives from different organizational levels to drive strategic technological integration and ensure comprehensive member-focused digital evolution.
Elevate Your Organisation’s Digital Literacy to Boost Member Engagement
Modern membership organisations face the challenge of bridging digital skill gaps while delivering personalised, seamless experiences. This article highlights key pain points such as adapting to continuous digital learning, managing diverse member competencies and mitigating risks linked to poor digital proficiency. Digital literacy is no longer optional but central to effective, data-driven engagement and operational success. Embracing adaptive digital competencies and ethical technology use can transform member relationships and foster sustained growth.
Colossus Systems offers a comprehensive SaaS platform tailored for membership organisations striving to enhance digital literacy impact. Our tools streamline member management, enable targeted communication, and support virtual training—empowering your team and members to build essential digital skills within a unified ecosystem. Benefit from our advanced analytics and customisable features to proactively address skill gaps and boost engagement across all demographics.
Discover how to transform your digital strategy with Colossus Systems today.
Explore personalised solutions designed to scale your organisation’s digital capabilities and secure a future-ready membership experience.
Take the first step towards developing a digitally literate, highly engaged community now by connecting with our experts. Harness technology to drive member satisfaction, operational excellence and long-term growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is digital literacy in the context of modern organisations?
Digital literacy in modern organisations refers to a comprehensive set of skills that go beyond basic technological competence, encompassing the ability to navigate digital environments, manage information effectively, and engage ethically with technology.
Why is digital literacy important for member engagement?
Digital literacy is crucial for member engagement as it enhances communication, fosters trust, and allows organisations to create personalised, meaningful experiences for members in increasingly digital environments.
How can organisations assess the digital literacy of their members?
Organisations can assess digital literacy through regular skills audits, identifying competency gaps, and implementing structured training programmes tailored to address both individual and collective learning needs.
What are the core components of modern digital literacy?
Core components of modern digital literacy include information literacy, digital content creation, online safety, problem-solving abilities, and effective communication, all of which are essential for navigating the complexities of today’s digital landscape.
Recommended
- What is Digital Engagement? Understanding Its Impact|CS
- Engagement Metrics Explained: Complete Guide for Organizations|CS
- Digital Communication Strategies for Member Organisations|CS
- Digital Advocacy: Driving Member Engagement Online|CS
- Understanding Music Marketing Analytics Explained - Blog - Music24.com