Complete Guide to Mindfulness in Education
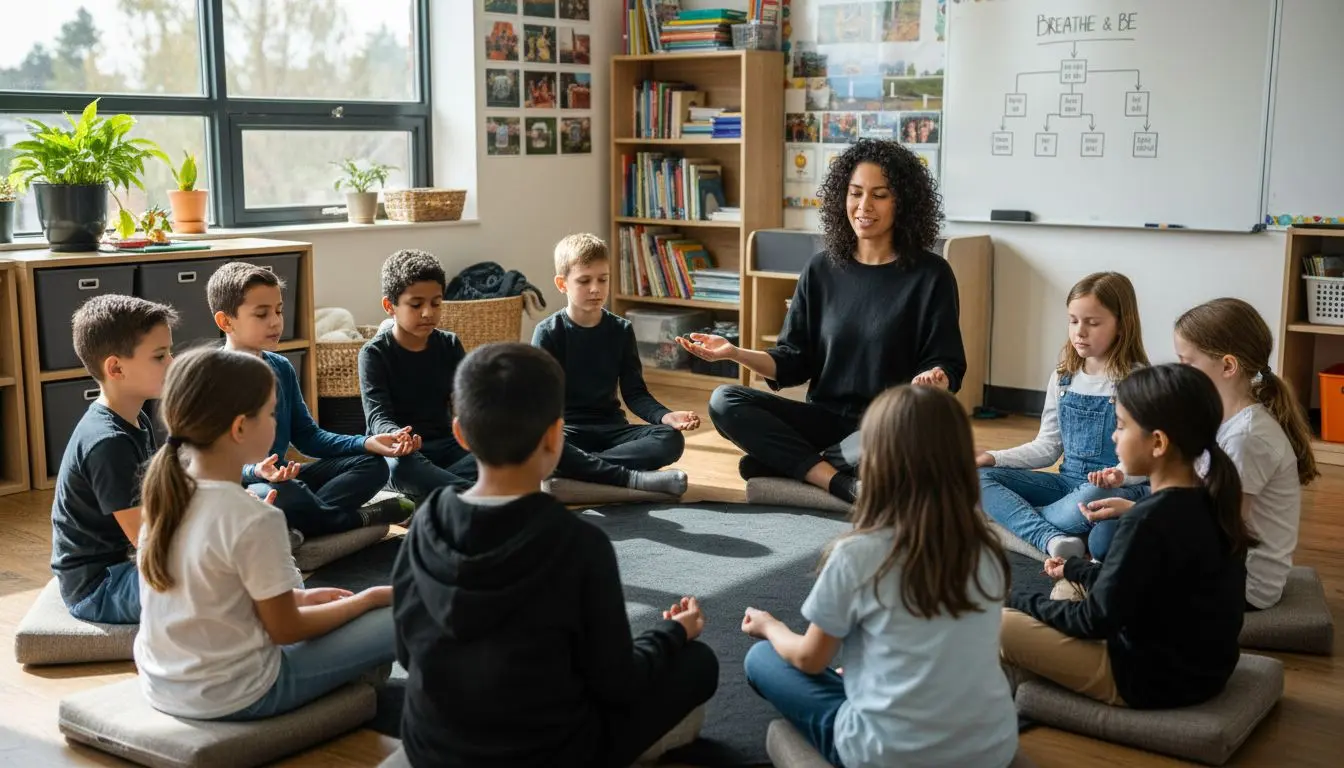

Nearly 70 percent of students experience overwhelming stress from academic demands, yet effective tools to manage these pressures remain surprisingly scarce. Mindfulness in schools is reshaping how students and teachers approach emotional challenges, focus, and classroom connection. Discover how simple habits like focused breathing and guided reflection can help young minds stay calm, improve attention, and build resilience for both learning and life beyond school.
Table of Contents
- Defining Mindfulness in Educational Settings
- Core Practices and Delivery Approaches
- Benefits for Students and Educators
- Implementing Mindfulness in Organizations
- Challenges, Risks, and Ethical Concerns
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Mindfulness Enhances Learning | Mindfulness practices improve emotional regulation, reduce stress, and foster cognitive skills, creating a more conducive learning environment. |
| Diverse Practices Required | A variety of mindfulness techniques, including meditation, breathing exercises, and movement, should be integrated into educational settings for optimal student benefits. |
| Critical for Educators | Educators benefit from mindfulness as it reduces burnout and enhances classroom management, fostering a compassionate environment for students. |
| Strategic Implementation Needed | Successful mindfulness adoption requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing training to overcome challenges and ensure sustainability. |
Defining Mindfulness in Educational Settings
Mindfulness represents a transformative approach to learning that goes far beyond traditional academic strategies. According to Wikipedia, mindfulness in education involves practices specifically designed to help students calm their minds, develop emotional intelligence, and enhance critical cognitive skills.
At its core, mindfulness is about cultivating present-moment awareness and creating mental space for students to process information more effectively. ISN Education highlights that these practices provide learners with powerful techniques to reduce academic anxiety and remain grounded during high-stress educational environments.
Key characteristics of mindfulness in educational settings include:
- Developing emotional regulation skills
- Improving attention and concentration
- Reducing stress and anxiety
- Enhancing problem-solving capabilities
- Fostering compassion and empathy among students
Practical mindfulness approaches in classrooms typically involve structured activities like guided breathing exercises, meditation techniques, and reflective practices that help students disconnect from distractions and reconnect with their internal experiences. By integrating these strategies, educational institutions can create more supportive, responsive learning environments that prioritise students’ mental and emotional well-being alongside academic achievement.
Core Practices and Delivery Approaches
Mindfulness practices in educational settings encompass a diverse range of techniques designed to support students’ mental and emotional well-being. Teacher Educator highlights that effective mindfulness programs typically include structured approaches such as deep breathing exercises, guided meditation, and mindful awareness techniques that help students develop crucial resilience and coping strategies.
Movement-based practices offer another powerful dimension to mindfulness education. According to Transpersonal Psychology, incorporating physical activities like yoga and tai chi can significantly enhance students’ body awareness and concentration, contributing to holistic cognitive development.
Key delivery approaches for mindfulness in educational contexts include:
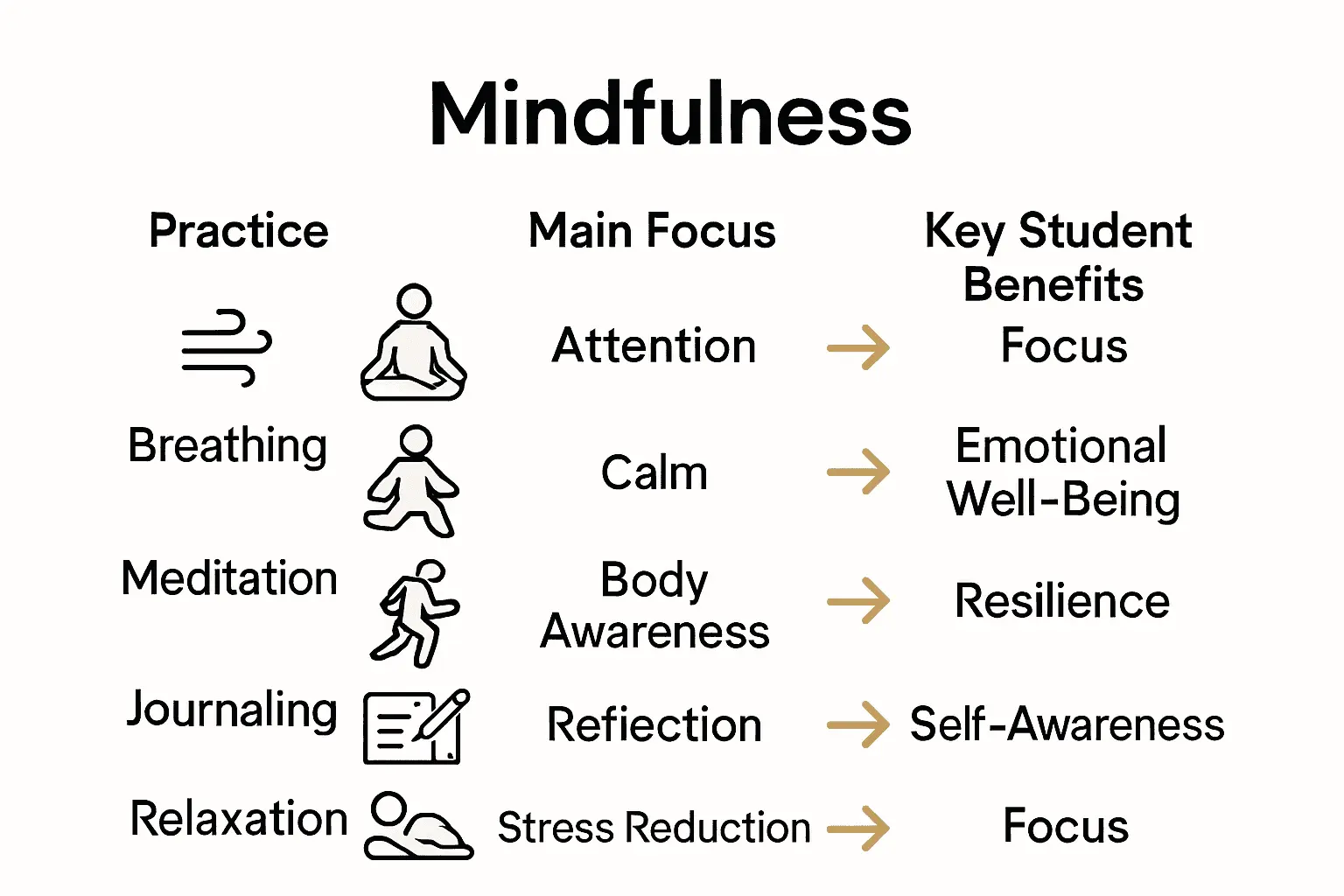
Here’s a summary of key mindfulness practices and their core benefits for students:
| Practice | Main Focus | Key Student Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Guided breathing exercises | Calmness Stress reduction |
Reduced anxiety |
| Short classroom meditation | Focus Presence |
Improved concentration |
| Mindful movement (yoga, tai chi) | Physical awareness | Enhanced body-mind connection |
| Reflection and journaling | Self-reflection Clarity |
Increased self-awareness |
| Structured relaxation techniques | Emotional regulation | Better emotional self-control |
- Classroom-based short meditation sessions
- Integrated mindfulness breaks during academic activities
- Structured breathing and relaxation techniques
- Mindful movement and physical awareness exercises
- Reflection and journaling practices
Successful implementation requires a nuanced approach that considers age-appropriate techniques, creates a supportive environment, and allows students to gradually develop their mindfulness skills. Educators play a critical role in modeling these practices, demonstrating authenticity, and creating safe spaces where students can explore their inner experiences without judgment or pressure. By approaching mindfulness as a skill to be learned and practiced, rather than a rigid prescription, schools can help students build lifelong emotional regulation and self-awareness tools.
Benefits for Students and Educators
Mindfulness practices offer transformative benefits for both students and educators, creating a more supportive and emotionally intelligent learning environment. International Research Journal of Multidisciplinary and Technological Sciences research reveals significant positive impacts, including improved emotional regulation, reduced stress and anxiety, enhanced focus, and increased empathy among students.
For students, these practices provide critical cognitive and emotional tools. According to ISN Education, mindfulness empowers learners to better regulate their emotions, leading to improved attention and overall cognitive capabilities in the classroom. This emotional intelligence translates into more resilient, self-aware, and adaptable learners.
Key benefits for students include:
- Enhanced emotional self-regulation
- Reduced academic stress and anxiety
- Improved concentration and cognitive performance
- Increased empathy and social awareness
- Better conflict resolution skills
For educators, mindfulness practices offer equally compelling advantages. Teachers who integrate these techniques experience reduced professional burnout, improved classroom management, and a deeper connection with their students. By modeling emotional intelligence and self-awareness, educators create a more compassionate, supportive learning environment that nurtures both academic and personal growth. The ripple effect of mindfulness extends beyond individual classrooms, potentially transforming entire educational cultures towards more holistic, student-centered approaches.

Implementing Mindfulness in Organizations
Organizational mindfulness requires a strategic and comprehensive approach that goes beyond simple implementation. Academia Today highlights the significant challenges institutions face, including resource limitations, faculty resistance, and complex logistical considerations that demand careful navigation.
Teacher Educator emphasizes the critical importance of providing robust, evidence-based research and compelling success stories to address potential resistance from educators and stakeholders. This approach helps legitimize mindfulness as a valuable organizational strategy rather than a passing trend.
Key strategies for successful mindfulness implementation include:
- Conducting comprehensive needs assessments
- Developing tailored training programmes
- Creating dedicated mindfulness spaces
- Integrating practices into existing organisational structures
- Establishing measurable implementation metrics
Successful implementation requires a multi-layered approach that recognizes mindfulness as a cultural transformation rather than a standalone programme. Organizations must cultivate leadership buy-in, provide ongoing training and support, and create an environment that normalizes emotional intelligence and self-awareness. This holistic approach ensures that mindfulness becomes an embedded practice, not just a superficial intervention, ultimately fostering more resilient, adaptive, and emotionally intelligent organisational cultures.
Challenges, Risks, and Ethical Concerns
Mindfulness implementation in educational settings presents complex challenges that require nuanced understanding and strategic navigation. Journal of Research and Technology in Teacher Development research identifies critical barriers including significant resource constraints, the critical need for comprehensive stakeholder engagement, and persistent resistance from educators stemming from insufficient training and awareness.
According to Transpersonal Psychology, the landscape of mindfulness adoption is fraught with skepticism about its effectiveness, time limitations, and institutional inertia. These challenges demand meticulous planning, robust evidence-based approaches, and sustained institutional commitment.
Key ethical and implementation challenges include:
- Potential for cultural misappropriation
- Ensuring voluntary participation
- Protecting students’ psychological safety
- Managing diverse individual responses
- Maintaining confidentiality during practices
- Addressing potential triggering experiences
Navigating these challenges requires a sophisticated, trauma-informed approach that prioritizes individual autonomy, respects diverse psychological backgrounds, and creates flexible, inclusive mindfulness frameworks. Organizations must develop comprehensive consent protocols, provide opt-out mechanisms, offer professional training for facilitators, and continuously evaluate the psychological impact of mindfulness interventions to ensure they genuinely support rather than potentially harm participants.
Enhance Mindfulness Initiatives with Seamless Member Engagement
Implementing mindfulness practices in education comes with challenges such as resource constraints, the need for ongoing training, and fostering emotional well-being at scale. The article highlights the importance of tailored approaches, emotional regulation support, and effective organisational strategies to create lasting impact. For organisations looking to build these supportive environments, managing events, training sessions, and communications can quickly become complex.
At Colossus Systems we understand the necessity of creating streamlined, customisable solutions to support mindfulness programmes and engagement efforts within membership organisations and educational institutions. Our platform offers unified tools for event planning, virtual training management, member communications, and customer relationship management all designed to help you nurture emotional intelligence and build resilient communities efficiently.
Take control of your mindfulness programme’s success today become the organisation that empowers learners and educators alike through effective engagement and management. Discover how easy it is to integrate mindful practices with our digital tools by reaching out through our contact page.
Ready to transform your education or membership organisation through mindful engagement Discover the difference with Colossus Systems where your goals for emotional well-being and operational excellence come together. Connect with us now at https://colossus.systems/contact-us/ and start creating meaningful change immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is mindfulness in education?
Mindfulness in education refers to practices aimed at helping students become more aware of the present moment, improving their emotional intelligence and cognitive abilities, and reducing academic stress and anxiety.
How can mindfulness practices benefit students?
Mindfulness practices can enhance emotional self-regulation, improve concentration, reduce academic stress, and increase students’ empathy and social awareness, contributing to a more supportive learning environment.
What are some core mindfulness practices used in educational settings?
Core mindfulness practices include guided breathing exercises, short classroom meditations, mindful movement (like yoga and tai chi), reflection and journaling, and structured relaxation techniques.
What challenges might educators face when implementing mindfulness in the classroom?
Challenges include resource limitations, faculty resistance, the need for comprehensive training, cultural sensitivity issues, and ensuring the psychological safety of students during mindfulness practices.