Meeting Compliance Requirements: Complete Guide for Organisations

More than 80 percent of british organisations report facing new compliance requirements every year, forcing leaders to rethink how they manage their legal and ethical responsibilities. Staying compliant is more than a box-ticking exercise—it shapes reputation and trust in an increasingly complex regulatory world. By understanding exactly what defines compliance for british organisations, you can better prepare to adapt quickly, minimise risk, and meet stakeholder expectations with confidence.
Table of Contents
- Defining Compliance Requirements For Organisations
- Key Legal And Regulatory Frameworks
- Types Of Compliance Relevant To Membership Bodies
- Essential Steps To Achieve Compliance
- Common Compliance Risks And How To Avoid Them
- Implementing Best Practices For Ongoing Compliance
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive Compliance Requirements | Organisations must adhere to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards from various sources to enhance accountability and minimise risks. |
| Dynamic Legal Frameworks | Developing adaptive compliance strategies is essential for navigating evolving legal landscapes and ensuring organisational integrity. |
| Tailored Approaches for Membership Bodies | Membership organisations require unique compliance frameworks that address governance, financial reporting, and member rights to maintain trust. |
| Ongoing Compliance Best Practices | A proactive and continuous approach to compliance, including regular audits and staff training, is crucial for organisational resilience and stakeholder confidence. |
Defining Compliance Requirements for Organisations
Compliance represents a strategic framework through which organisations systematically manage their legal, regulatory, and ethical obligations. Compliance requirements are comprehensive directives that outline the specific standards, rules, and protocols organisations must adhere to across their operational landscape. These requirements emerge from multiple sources including governmental regulations, industry standards, internal policies, and voluntary commitments.
According to Quality.org, compliance obligations are critically defined by frameworks like ISO 14001, which emphasise the need for organisations to meticulously identify and fulfil both mandatory legal requirements and additional voluntary commitments. This approach ensures organisations not only meet minimum legal standards but also proactively address external expectations and stakeholder interests.
Compliance requirements typically encompass several key dimensions:
- Legal Compliance: Adhering to national and local legislation
- Industry Standards: Meeting sector-specific regulatory frameworks
- Ethical Guidelines: Maintaining professional conduct and integrity
- Risk Management: Implementing processes to mitigate potential regulatory breaches
- Reporting Mechanisms: Creating transparent documentation of compliance activities
Successful implementation of comprehensive compliance requirements demands a holistic approach. Organisations must develop robust internal systems that continuously monitor regulatory landscapes, assess organisational practices, and swiftly adapt to emerging legal and ethical standards. This dynamic approach transforms compliance from a mere administrative burden into a strategic organisational capability that enhances reputation, minimises legal risks, and demonstrates professional accountability.
Key Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Legal and regulatory frameworks represent the fundamental infrastructure that governs organisational behaviour, establishing critical boundaries and expectations for business operations across diverse sectors. These comprehensive systems of rules and guidelines provide structured mechanisms for ensuring accountability, protecting stakeholder interests, and maintaining ethical standards in commercial and institutional environments.
According to UN-iLibrary, establishing sound legal frameworks is paramount for building trust between businesses and consumers, particularly in complex digital ecosystems. These frameworks must comprehensively address crucial areas such as electronic transactions, consumer protection, data security, and emerging technological interactions.
Key legal and regulatory frameworks typically encompass multiple critical domains:
- Corporate Governance: Rules defining organisational leadership and accountability
- Financial Regulations: Standards governing fiscal reporting and transparency
- Data Protection: Guidelines ensuring privacy and security of sensitive information
- Employment Law: Regulations defining workplace rights and organisational responsibilities
- Industry-Specific Compliance: Sector-tailored regulatory requirements
Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes requires organisations to develop dynamic, adaptive compliance strategies. Successful implementation involves continuous monitoring of legislative changes, proactive risk management, and creating robust internal systems that can swiftly integrate new regulatory requirements. This approach transforms legal compliance from a static obligation into a strategic organisational capability that supports sustainable growth and maintains professional integrity.

Types of Compliance Relevant to Membership Bodies
Membership body compliance represents a multifaceted framework of regulatory obligations that organisations must navigate to maintain legal, ethical, and operational integrity. These compliance requirements are unique to membership-based entities, reflecting the complex interactions between organisational structures, member rights, and broader regulatory landscapes.
According to OECD, designing effective legal frameworks for membership organisations requires careful consideration of their distinctive operational characteristics. The research highlights the critical need for tailored compliance approaches that address the specific governance, financial, and operational challenges faced by these entities.
Types of compliance relevant to membership bodies encompass several critical domains:
- Governance Compliance: Regulations governing organisational decision-making processes
- Financial Reporting: Standards for transparent financial management and reporting
- Data Protection: Requirements for managing member personal information
- Ethical Standards: Guidelines ensuring fair treatment and representation of members
- Operational Transparency: Regulations mandating clear communication and accountability
- Tax and Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to specific legal obligations based on organisational structure
Successful navigation of these compliance requirements demands a proactive and comprehensive approach. Learn more about membership management to understand how organisations can effectively integrate these complex compliance frameworks into their operational strategies. By developing robust internal systems that continuously monitor and adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes, membership bodies can transform compliance from a potential burden into a strategic advantage that enhances organisational credibility and member trust.
Essential Steps to Achieve Compliance
Compliance achievement is a strategic process that requires systematic planning, continuous monitoring, and proactive management across organisational operations. Successfully navigating complex regulatory landscapes demands a structured approach that transforms compliance from a potential administrative burden into a robust organisational capability.
According to Quality.org, organisations must meticulously identify and integrate applicable legal requirements into their management systems, ensuring comprehensive addressing of external issues and meeting stakeholder expectations. This approach emphasises the critical importance of creating dynamic frameworks that can adapt to evolving regulatory environments.
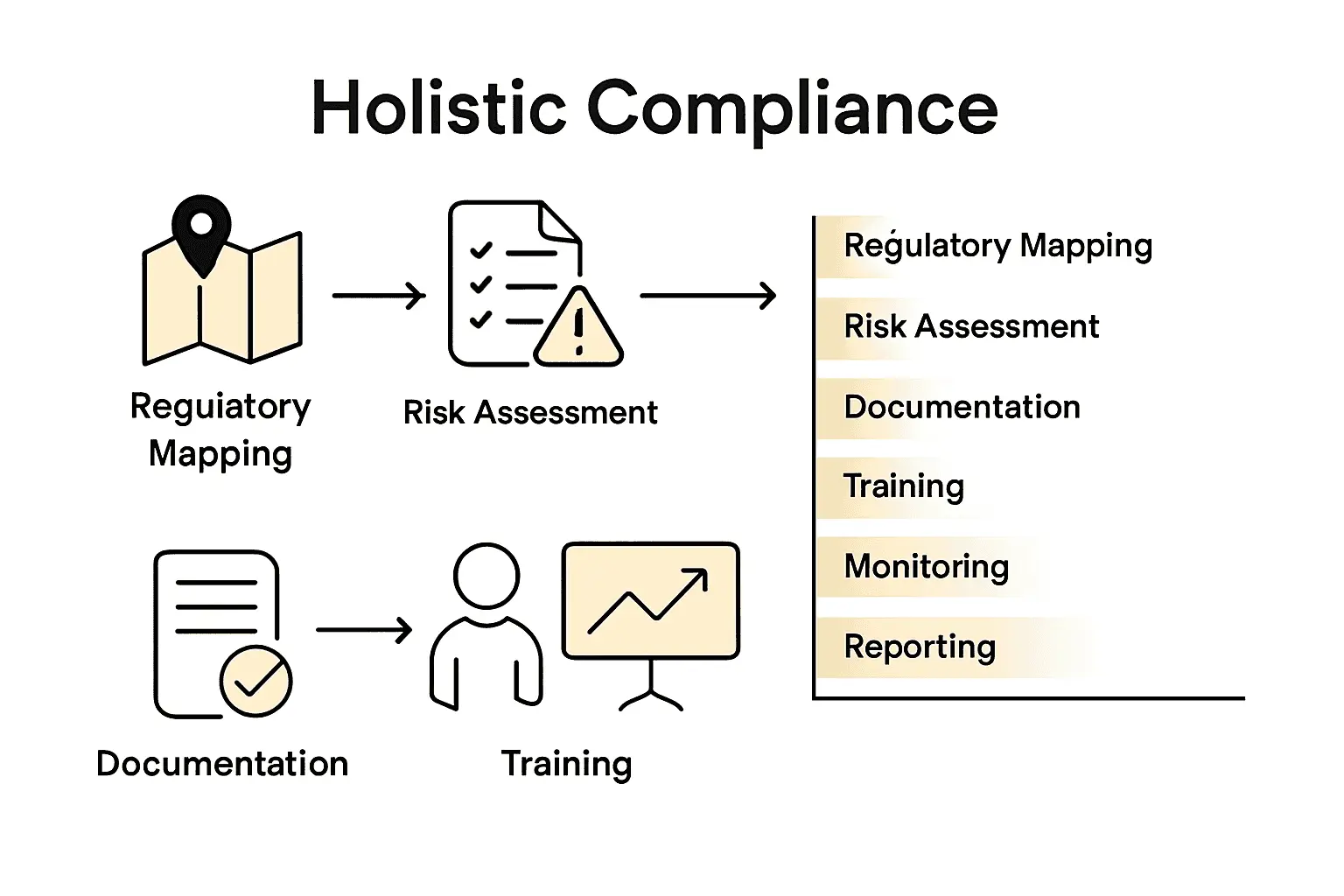
Essential steps to achieve comprehensive compliance include:
- Regulatory Mapping: Conduct thorough identification of all applicable legal and regulatory requirements
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate potential compliance gaps and vulnerabilities within current organisational processes
- Documentation Development: Create comprehensive policies and procedural guidelines
- Training Programmes: Implement robust staff education initiatives on compliance requirements
- Monitoring Mechanisms: Establish continuous internal audit and review systems
- Reporting Frameworks: Develop transparent reporting processes for tracking compliance status
Learn more about membership management to understand how technology can streamline these compliance processes. By adopting a holistic, proactive approach, organisations can transform compliance from a reactive obligation into a strategic asset that enhances organisational resilience, protects stakeholder interests, and demonstrates professional integrity.
Common Compliance Risks and How to Avoid Them
Compliance risks represent potential vulnerabilities that can compromise an organisation’s legal and ethical standing, potentially resulting in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Understanding these risks is crucial for developing proactive strategies that protect organisational integrity and maintain stakeholder confidence.
According to UN-iLibrary, organisations face substantial challenges in building trust, particularly within digital ecosystems where complex legal and regulatory frameworks are constantly evolving. The research emphasises the critical need for comprehensive risk mitigation strategies that address consumer protection and organisational accountability.
Common compliance risks organisations encounter include:
- Data Privacy Breaches: Inadequate protection of member and stakeholder personal information
- Financial Mismanagement: Insufficient transparency in fiscal reporting and transactions
- Regulatory Non-Alignment: Failure to adapt to changing legal requirements
- Ethical Misconduct: Lack of robust internal governance mechanisms
- Documentation Gaps: Incomplete or inconsistent compliance record-keeping
- Training Deficiencies: Insufficient staff understanding of compliance obligations
Event risk management strategies can provide additional insights into developing comprehensive risk mitigation approaches. By implementing systematic monitoring, continuous education, and adaptive compliance frameworks, organisations can transform potential risks into opportunities for demonstrating professional excellence and building long-term stakeholder trust.
Implementing Best Practices for Ongoing Compliance
Ongoing compliance is a dynamic process that demands continuous attention, strategic planning, and adaptive management across organisational infrastructure. Successfully maintaining compliance requires more than periodic reviews, instead necessitating a holistic approach that integrates regulatory awareness into the core operational fabric of the organisation.
According to UN-iLibrary, establishing robust legal and regulatory frameworks requires continuous legal reforms and strategic capacity-building initiatives. The research emphasises the critical importance of developing flexible mechanisms that can rapidly respond to evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging compliance challenges.
Key best practices for implementing ongoing compliance include:
- Proactive Monitoring: Continuously track regulatory changes and emerging legal requirements
- Regular Audits: Conduct systematic internal and external compliance assessments
- Technology Integration: Leverage digital tools for real-time compliance tracking
- Comprehensive Training: Develop ongoing educational programmes for staff
- Documentation Management: Maintain meticulous and up-to-date compliance records
- Cultural Embedding: Foster a compliance-focused organisational culture
- Adaptive Frameworks: Create flexible systems capable of rapid regulatory adaptation
Learn more about membership management to understand how technology can support these compliance strategies. By embracing a proactive, dynamic approach to compliance, organisations can transform regulatory requirements from potential challenges into opportunities for demonstrating professional excellence and building stakeholder trust.
Simplify Compliance and Empower Your Membership Organisation Today
Meeting complex compliance requirements is a significant challenge for membership organisations. The need to navigate governance compliance, data protection, financial transparency, and ethical standards can quickly overwhelm internal teams without the right tools. Managing regulatory risks and ongoing compliance demands a streamlined approach that reduces administrative burdens while maintaining operational transparency and accountability.
Colossus Systems offers a comprehensive SaaS platform designed specifically to help membership bodies transform compliance from a challenge into a strength. Our integrated tools enable you to automate member data protection, enforce governance protocols, and maintain clear financial records effortlessly. With features like advanced reporting, customised workflows, and secure payment integrations, your organisation can stay ahead of evolving compliance demands and build lasting trust with members. Start strengthening your compliance strategy now by connecting with our expert team at Contact Us. Discover how membership management technology at Colossus Systems can drive your compliance with confidence and ease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are compliance requirements for organisations?
Compliance requirements are comprehensive directives that outline the specific standards, rules, and protocols organisations must adhere to across their operations, emerging from governmental regulations, industry standards, internal policies, and voluntary commitments.
How can organisations effectively implement compliance requirements?
Organisations can effectively implement compliance requirements by developing robust internal systems, conducting regulatory mapping, assessing risks, creating comprehensive documentation, providing training, establishing monitoring mechanisms, and maintaining transparent reporting processes.
What are the common compliance risks faced by organisations?
Common compliance risks include data privacy breaches, financial mismanagement, regulatory non-alignment, ethical misconduct, documentation gaps, and training deficiencies, which can jeopardise legal and ethical standings.
What best practices should organisations follow for ongoing compliance?
Best practices for ongoing compliance include proactive monitoring of regulatory changes, regular audits, technology integration for compliance tracking, comprehensive staff training, meticulous documentation management, fostering a compliance-focused culture, and creating adaptive compliance frameworks.